The Multimedia Learning Hypothesis
Learning is effected when multiple representations of content is offered. Simply, using both words and pictures is more effective than providing words alone. Educators can adapt and use multimedia to enhance learning in a multitude of ways. Mayer, (2005) devised Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning stating “multimedia instructional messages that are designed in light of how the human mind works are more likely to lead to meaningful learning than those that are not”.
Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning (Mayer)
- There are two separate channels (audio and visual) for processing information (sometimes referred to as Dual-Coding Theory);
- Each channel has a limted (finite) capacity (Cognitive Load);
- Learning is an actice process of filtering, selecting, organizing, and integrating information based upon prior knowledge.
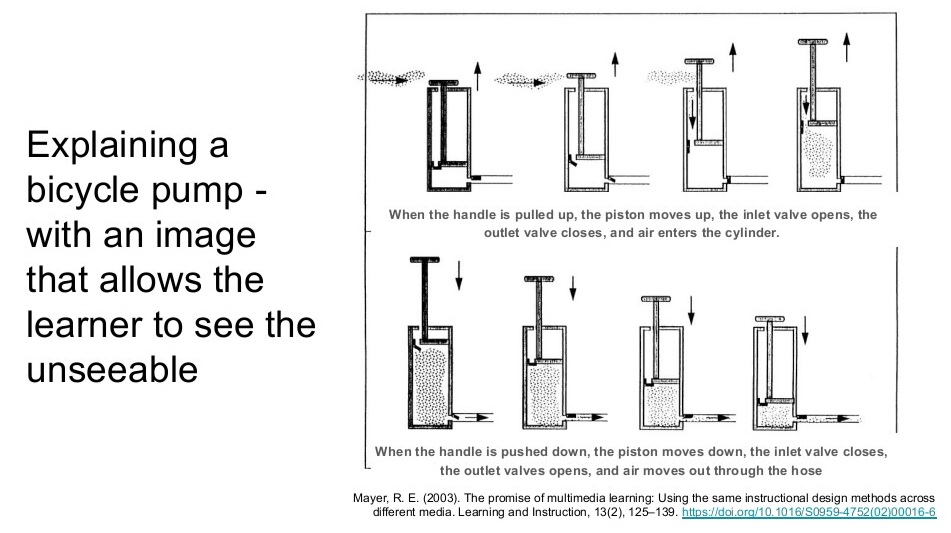
In a classic way, Meyer (2009) produces the example of explaining a bicycle pump. One using text only with the second incorporating multimedia. The point being literally illustrated below.
Explaining a bicycle pump – text alone
“When the handle is pulled up the piston moves up, the inlet valve opens, the outlet valve closes, and the air enters the cylinder. When the handle is pushed down, the piston moves down, the inlet valve closes, the outlet valves opens, and air moves out thorough the hose”.
For a more in-depth look at the principles of multimedia learning here is a presentation from Mayer.
Mayer, R.E. (2009). Multimedia Learning. Cambridge University Press.
Mayer, R. E. (2005). Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning. In R. E. Mayer (Ed.), The Cambridge handbook of multimedia learning (p. 31–48). Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511816819.004
Working with graphics
Within your practice you will create multimedia content for multiple reasons. Classroom lessons, workshops, or your online content can benefit from multimedia. UVic students are granted access to Microsoft and may use Adobe software in select computing facilities at UVic. More information can be found by contacting the helpdesk or onlineservices.uvic.ca.
As you will create diverse content there may be specialized programs you will utilize. Depending on what content you want to create there are different types of programs which potentially may be more suitable to your task. Raster graphic editors are programs that allows you to create and edit images and save them in one of many such as JPEG, PNG, and GIFand may be are more suitable for retouching, photo processing, photorealistic illustrations, collage, and illustrations drawn by hand.
Vector graphics editor software are often used for typography, logos, sharp-edged artistic illustrations, cartoons, clip art, complex geometric patterns, technical illustrations, diagramming and flowcharting. Comparison of vector graphics editors. Currently https://inkscape.org/ is free and popular.
Here are some popular tools you can create with.
- Microsoft Paint – native to Windows photo editing program for basic multimedia that is widely available and still used
- Microsoft PowerPoint – presentation software used extensively in K-12 to accompany classroom teaching has editing capabilities
- Adobe Creative Cloud – professional standard collection of 20+ services for photography, design, video, web, and where you can find Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign, Premiere and the pdf classic Acrobat.(UVic tutorial)
- Go further – try experimenting with some advanced web based freely available graphic creation tools online (Pixlr.com or Vectr.com or canva.com to start)
- Click here for an exhaustive list
Screensots

Capturing whatever is on your screen is another way to create content. Screenshots or screen grabs can be taken by pressing the ‘control’ and ‘print screen’ keys on windows computers. To edit, paste into a program like MS Paint. This site lists 6 other ways.
To take a screenshot on a Mac: Press command, shift, 4, allows you to drag your mouse and select what you want to screenshot and command, shift, 3 take a screenshot of the entire screen
To take a screenshot on an iOS phone – Hold volume up and side button
To take a screenshot on an Android phone – Hold volume down and power button
Finding graphics
Simple changes can help you customize your content to fit the exact content you need for your lesson or other needs. Finding graphics you are able to edit and remix on sites like creativecommons.org unsplash.com gives you a headstart and means you may not have to start from scratch. To save graphics or slides as picture files.
- right click image
- select save as picture
- select PNG or JPG
Image file size
When working with graphics, you should be conscious of the size of the files you are working with. As a general rule, images should be under one megabyte when sharing online
within virtual learning environments or on your blog (1080 pixels or less on the longest edge of the photo).
Tutorial on how to resize images on your Mac computer
App to resize image on Windows (quick demo)
Also see Adobe’s guide to resizing and cropping images.
Effects, filters and more manipulation

Photo by Pratik Chauhan on Unsplash
Adding interesting attributes to graphics may aid in making your content engaging. Apps are very common and many have overlapping features. Try some!
PowerPoint resources
How You Should Actually Be Using PowerPoint,
How To Make An Infographic In PowerPoint,


Leave a Reply